How Do You Ship Something Frozen

Shipping frozen goods presents a unique set of challenges due to the inherent sensitivity of perishable items. From maintaining the cold chain to ensuring safe transportation, there are numerous factors to consider when shipping frozen products. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of shipping frozen items, offering expert advice and insights to help you navigate the process effectively.
The Cold Chain Logistics
Maintaining the integrity of frozen goods throughout the shipping process is critical. The cold chain, a temperature-controlled supply chain, plays a vital role in ensuring the quality and safety of perishable items. Here’s an overview of the key considerations when it comes to cold chain logistics:
Temperature Control
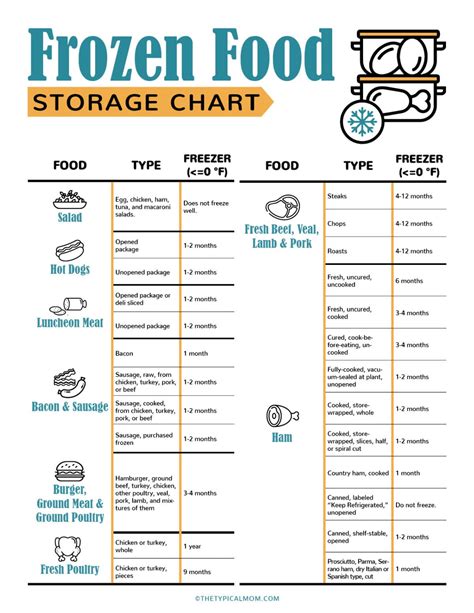
The foundation of any successful cold chain is temperature control. Frozen goods must be kept at a consistent temperature to prevent thawing and refreezing, which can lead to product degradation and safety risks. The specific temperature requirements vary depending on the product. For instance, frozen seafood typically requires temperatures below -18°C (-0.4°F), while frozen desserts may need temperatures around -25°C (-13°F) or lower.
| Product Category | Optimal Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Meat and Poultry | -18°C to -25°C (-0.4°F to -13°F) |
| Seafood | -18°C to -20°C (-0.4°F to -4°F) |
| Frozen Meals | -18°C to -25°C (-0.4°F to -13°F) |
| Ice Cream and Desserts | -25°C or lower (-13°F or lower) |

To achieve precise temperature control, specialized refrigeration units are employed. These units can be integrated into various transportation modes, such as refrigerated trucks, railcars, and cargo ships. Advanced temperature monitoring systems, often equipped with real-time data transmission capabilities, ensure that temperature fluctuations are detected and addressed promptly.
Packaging and Insulation
Proper packaging is essential to protect frozen goods during transit. Insulated containers or boxes are commonly used to maintain the cold chain. These containers are designed to minimize heat transfer, ensuring that the temperature inside remains stable. The choice of packaging material depends on factors such as the duration of the journey, the ambient temperature, and the specific product being shipped.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Boxes: Commonly used for short-distance shipments, EPS boxes offer excellent insulation properties and are cost-effective.
- Vacuum-Insulated Panels (VIPs): These high-performance panels provide superior insulation, making them suitable for long-haul shipments and maintaining ultra-low temperatures.
- Refrigerated Containers (REEFs): For containerized shipping, REEFs offer a controlled environment, ensuring consistent temperatures throughout the journey.
Transportation Options
The choice of transportation mode is crucial in maintaining the cold chain. Each mode has its advantages and considerations:
- Road Transportation: Refrigerated trucks are widely used for local and regional shipments. They offer flexibility and can be equipped with advanced temperature control systems.
- Rail Transport: For longer distances, rail transportation provides a cost-effective and energy-efficient option. Specialized railcars with refrigeration units ensure the cold chain is maintained.
- Air Freight: Air transport is ideal for time-sensitive shipments. While it may be more expensive, it offers rapid delivery, minimizing the risk of temperature fluctuations.
- Sea Freight: Container ships are commonly used for international shipments. Refrigerated containers (REEFs) can be stacked and transported, ensuring a controlled environment during the voyage.
Shipping Logistics and Best Practices

Effective shipping logistics are crucial to ensure the safe delivery of frozen goods. Here are some key practices to consider:
Product Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage of frozen goods are essential to prevent damage and maintain quality. Here are some best practices:
- Ensure that the warehouse or storage facility maintains the required temperature. Regularly monitor and adjust temperatures to avoid fluctuations.
- Handle frozen goods with care to prevent accidental thawing or physical damage. Use appropriate equipment and follow safe handling procedures.
- Implement first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory management to ensure that older batches are used or shipped first, reducing the risk of product degradation.
Documentation and Compliance
Accurate and comprehensive documentation is vital when shipping frozen goods. This includes:
- Preparing detailed packing lists and labels, clearly indicating the contents and any special handling requirements.
- Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, such as food safety regulations and international shipping guidelines.
- Maintaining proper paperwork for customs clearance, especially when shipping internationally.
Tracking and Monitoring
Real-time tracking and monitoring systems are essential to ensure the integrity of frozen goods during transit. These systems provide valuable insights, including:
- Temperature monitoring: Advanced sensors and data loggers track temperature fluctuations, alerting stakeholders to any deviations from the desired range.
- Location tracking: GPS-enabled tracking systems provide real-time updates on the shipment's location, helping to optimize delivery routes and ensure timely deliveries.
- Condition monitoring: Some advanced tracking systems can monitor additional parameters, such as humidity, shock, and tilt, providing a comprehensive overview of the shipment's condition.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Despite careful planning, unexpected events can occur during shipping. Implementing robust risk management strategies is crucial:
- Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards and develop contingency plans.
- Have backup transportation options in place to minimize delays in case of equipment failures or unforeseen circumstances.
- Implement quality control measures to identify and address any issues promptly. This includes regular audits, inspections, and feedback mechanisms.
Future Trends and Innovations
The shipping industry is continuously evolving, and advancements in technology and logistics are shaping the future of frozen goods transportation. Here are some key trends and innovations to watch:
Sustainable Shipping Solutions
With a growing emphasis on environmental sustainability, the shipping industry is exploring eco-friendly solutions. This includes the development of:
- Electric refrigerated trucks and railcars, reducing carbon emissions and minimizing the environmental impact of transportation.
- Sustainable packaging materials, such as biodegradable insulation, to reduce waste and promote a circular economy.
- Energy-efficient refrigeration systems, optimizing power consumption while maintaining precise temperature control.
Advanced Data Analytics
The integration of advanced data analytics and machine learning is revolutionizing shipping logistics. These technologies enable:
- Predictive analytics for more accurate demand forecasting, optimizing inventory levels and reducing waste.
- Real-time data-driven decision-making, allowing for dynamic route optimization and efficient resource allocation.
- Enhanced visibility and transparency throughout the supply chain, improving collaboration and reducing delays.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is transforming supply chain management by providing a secure and transparent record of transactions. In the context of shipping frozen goods, blockchain can:
- Enhance food safety by tracking the origin and journey of perishable items, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Improve traceability, allowing stakeholders to quickly identify and address any issues or recalls.
- Streamline customs processes by providing a tamper-proof record of shipping documents, reducing delays and administrative burdens.
Conclusion
Shipping frozen goods requires a meticulous approach, from maintaining the cold chain to implementing best practices in logistics. By understanding the unique challenges and employing the right strategies, you can ensure the safe and timely delivery of perishable items. With continuous advancements in technology and logistics, the future of frozen goods shipping looks promising, offering improved efficiency, sustainability, and transparency.
What are the key challenges when shipping frozen goods internationally?
+Shipping frozen goods internationally presents additional challenges, including navigating complex customs regulations, ensuring compliance with food safety standards, and managing the longer transit times. It requires meticulous planning, collaboration with specialized logistics providers, and thorough documentation to ensure a seamless and compliant process.
How can I ensure the quality of frozen goods during transit?
+To maintain the quality of frozen goods, it’s crucial to follow best practices such as proper packaging, maintaining a stable temperature, and minimizing exposure to temperature fluctuations. Regularly monitoring the shipment’s condition and implementing quality control measures can help identify and address any issues promptly.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when shipping frozen goods?
+Common mistakes include inadequate temperature control, improper packaging, and failure to consider the specific requirements of different frozen goods. It’s essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the product, its temperature needs, and the best practices for handling and shipping to avoid these pitfalls.
How can I optimize my shipping costs while maintaining the cold chain?
+Optimizing shipping costs while maintaining the cold chain requires a balanced approach. Consider factors such as transportation mode, packaging efficiency, and route optimization. By leveraging technology, data analytics, and sustainable practices, you can strike a balance between cost-effectiveness and maintaining the integrity of frozen goods.
What are the benefits of implementing blockchain technology in frozen goods shipping?
+Blockchain technology offers enhanced transparency, traceability, and security in frozen goods shipping. It improves food safety, streamlines customs processes, and provides a tamper-proof record of transactions, reducing administrative burdens and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.



