Stock Turn Ratio Formula

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding and Calculating the Stock Turn Ratio
The stock turn ratio, also known as inventory turnover or stock turnover ratio, is a crucial metric in financial analysis and inventory management. It provides valuable insights into a company's efficiency in managing its inventory, ensuring optimal stock levels, and minimizing costs. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of stock turn ratios, exploring their significance, calculation methods, and practical applications.
Whether you're an investor, business owner, or financial analyst, understanding the stock turn ratio is essential for making informed decisions and maintaining a competitive edge in today's dynamic business landscape.
Unveiling the Significance of Stock Turn Ratios

The stock turn ratio is a fundamental tool for assessing a company's inventory management practices and financial health. By analyzing this ratio, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into various aspects of a business's operations.
Here's a breakdown of why stock turn ratios matter:
1. Inventory Efficiency
A high stock turn ratio indicates that a company is effectively managing its inventory. It suggests that the business is able to sell its products quickly, reducing the risk of obsolete or outdated stock. This efficiency translates to lower storage costs, improved cash flow, and a more responsive supply chain.
2. Financial Performance
The stock turn ratio is a key indicator of a company’s financial performance. It reflects the ability to generate revenue from inventory investments. A higher ratio suggests better utilization of assets, leading to increased profitability. Conversely, a low ratio may indicate inefficiencies or excessive inventory levels, impacting cash flow and profitability.
3. Risk Management
Understanding the stock turn ratio helps businesses identify and mitigate risks associated with inventory management. It allows companies to assess the likelihood of stock obsolescence, excessive stockholding costs, and potential disruptions in the supply chain. By monitoring this ratio, businesses can take proactive measures to optimize inventory levels and minimize risks.
4. Benchmarking and Comparison
Stock turn ratios provide a valuable benchmark for comparing a company’s performance against industry averages and competitors. This comparison enables businesses to identify areas for improvement, adopt best practices, and make strategic decisions to enhance their competitive position.
Calculating the Stock Turn Ratio: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we've established the significance of stock turn ratios, let's explore the calculation process in detail. The formula for calculating the stock turn ratio is straightforward, but it requires accurate data and careful consideration of various factors.
1. Gather Necessary Data
To calculate the stock turn ratio, you’ll need the following information:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a specific period (e.g., quarterly or annually)
- Average Inventory Value for the same period
COGS represents the direct costs incurred in producing or acquiring the goods sold. It includes the cost of raw materials, labor, and overhead expenses directly related to production. Average inventory value is calculated by taking the average of the beginning and ending inventory values for the specified period.
2. Calculate the Stock Turn Ratio
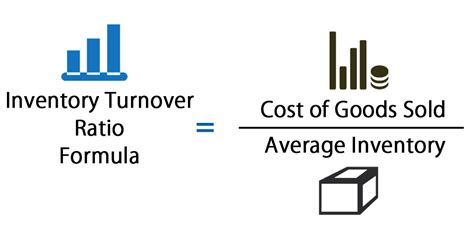
The formula for the stock turn ratio is as follows:
Stock Turn Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) / Average Inventory Value
By dividing the COGS by the average inventory value, you obtain a ratio that represents the number of times the inventory is sold or turned over during the specified period. A higher ratio indicates faster inventory turnover, while a lower ratio suggests slower turnover.
3. Interpret the Results
Once you’ve calculated the stock turn ratio, it’s essential to interpret the results in the context of your industry and specific business goals. Here’s a general guideline for interpreting stock turn ratios:
- High Stock Turn Ratio: A ratio above 5 or 6 indicates that the company is efficiently managing its inventory. It suggests that the business is selling its products quickly, reducing the risk of excess inventory and associated costs.
- Low Stock Turn Ratio: A ratio below 2 or 3 may indicate inefficiencies in inventory management. It could suggest excessive stock levels, slow-moving products, or potential issues with demand forecasting.
Factors Influencing Stock Turn Ratios
While the stock turn ratio provides valuable insights, it's essential to consider the factors that can influence its calculation and interpretation. Understanding these factors helps in making accurate assessments and adjustments to inventory management strategies.
1. Industry and Product Characteristics
Different industries and product types have varying stock turn ratios. For example, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industries, such as food and beverages, typically have higher stock turn ratios due to the nature of their products and consumer demand. On the other hand, industries with longer production cycles or customized products may have lower ratios.
2. Demand Variability
Fluctuations in demand can significantly impact stock turn ratios. High demand variability, especially in industries with seasonal or unpredictable trends, may result in lower ratios as businesses adjust their inventory levels to meet varying customer needs.
3. Lead Time and Supply Chain
The efficiency of a company’s supply chain, including lead times for ordering and receiving inventory, plays a crucial role in stock turn ratios. Longer lead times can impact the ability to respond quickly to changes in demand, potentially resulting in lower ratios.
4. Pricing and Promotions
Pricing strategies and promotional activities can influence stock turn ratios. Companies may adjust their pricing to stimulate demand and improve turnover, especially for slow-moving products. Additionally, promotional campaigns can boost sales and impact the overall ratio.
Optimizing Stock Turn Ratios: Strategies for Success

Achieving optimal stock turn ratios requires a strategic approach to inventory management. By implementing effective strategies, businesses can enhance their inventory efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall financial performance.
1. Demand Forecasting and Planning
Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for optimizing stock turn ratios. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer behavior, businesses can make informed decisions about inventory levels. Effective demand planning ensures that inventory aligns with expected demand, reducing the risk of excess stock or stockouts.
2. Just-in-Time Inventory Management
Adopting just-in-time (JIT) inventory management principles can significantly improve stock turn ratios. JIT involves minimizing inventory levels by synchronizing production and delivery with customer demand. This approach reduces holding costs, minimizes waste, and improves overall inventory efficiency.
3. Efficient Supply Chain Management
Optimizing the supply chain is essential for achieving higher stock turn ratios. Businesses should focus on streamlining processes, reducing lead times, and improving communication with suppliers. Efficient supply chain management ensures that inventory is received promptly, reducing the risk of stockouts and improving overall turnover.
4. Inventory Optimization Techniques
Implementing inventory optimization techniques, such as ABC analysis and economic order quantity (EOQ) calculations, can help businesses prioritize inventory management. ABC analysis categorizes inventory into A, B, and C items based on their value and turnover, allowing businesses to focus on high-value, fast-moving items. EOQ calculations determine the optimal order quantity to minimize costs associated with ordering and holding inventory.
Case Study: Improving Stock Turn Ratios in Retail
Let's explore a practical example of how a retail business can improve its stock turn ratio through strategic inventory management.
Imagine a retail store specializing in fashion accessories. The store's management has noticed that its stock turn ratio has been consistently below the industry average, indicating potential inefficiencies in inventory management.
Strategy 1: Demand Forecasting and Planning
The management team decides to enhance their demand forecasting capabilities by investing in advanced analytics tools. They analyze historical sales data, customer behavior, and market trends to develop more accurate demand forecasts. By aligning inventory levels with expected demand, they aim to reduce excess stock and improve turnover.
Strategy 2: Just-in-Time Inventory Management
To implement JIT principles, the store establishes closer collaboration with its suppliers. They negotiate shorter lead times and more frequent deliveries, ensuring that inventory is replenished promptly. By reducing the time between ordering and receiving inventory, the store can respond quickly to changes in demand and improve its stock turn ratio.
Strategy 3: Efficient Store Layout and Display
The management team also recognizes the importance of efficient store layout and product display. They reorganize the store layout to enhance product visibility and customer flow. By placing fast-moving items in high-traffic areas and ensuring effective product display, they encourage impulse purchases and improve overall sales.
Results
After implementing these strategies, the retail store sees a significant improvement in its stock turn ratio. By optimizing demand forecasting, adopting JIT principles, and enhancing store layout, the store achieves a higher ratio, reducing excess inventory and improving cash flow. The management team continues to monitor and refine their inventory management practices to maintain optimal stock turn ratios.
The Future of Stock Turn Ratios: Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, the field of inventory management is evolving rapidly. Here are some trends and innovations shaping the future of stock turn ratios:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms are revolutionizing inventory management. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, including sales patterns, customer behavior, and market trends, to provide accurate demand forecasts and optimize inventory levels. By leveraging AI, businesses can achieve even higher stock turn ratios and improve overall inventory efficiency.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Inventory Tracking
The integration of IoT devices and sensors in inventory management is transforming the way businesses track and monitor their stock. Smart inventory tracking systems provide real-time data on inventory levels, location, and movement. This enables businesses to make data-driven decisions, optimize replenishment processes, and improve overall stock turn ratios.
3. Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology is gaining traction in supply chain management, offering increased transparency and traceability. By implementing blockchain solutions, businesses can track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, from raw materials to final delivery. This improved visibility enhances inventory management, reduces lead times, and contributes to higher stock turn ratios.
Conclusion
Understanding and calculating the stock turn ratio is a critical aspect of financial analysis and inventory management. By analyzing this ratio, businesses can gain valuable insights into their inventory efficiency, financial performance, and risk management. Through strategic inventory management practices and leveraging technological innovations, companies can optimize their stock turn ratios, improve profitability, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of industry trends and adopting innovative inventory management strategies will be crucial for long-term success. By embracing the power of data-driven decision-making and technological advancements, businesses can unlock the full potential of their inventory and achieve optimal stock turn ratios.
How often should stock turn ratios be calculated and monitored?
+
Stock turn ratios should be calculated and monitored on a regular basis, typically on a quarterly or annual basis. However, depending on the industry and business needs, some companies may choose to calculate and analyze stock turn ratios more frequently, such as on a monthly or even weekly basis. Regular monitoring allows businesses to identify trends, make timely adjustments, and ensure optimal inventory management.
Can a high stock turn ratio always be considered positive?
+
While a high stock turn ratio generally indicates efficient inventory management, it’s important to consider the industry and business context. Some industries, such as fashion retail, may naturally have higher stock turn ratios due to the nature of their products and consumer demand. However, in other industries, a very high stock turn ratio may suggest that the company is carrying insufficient inventory, potentially leading to stockouts and lost sales opportunities. Therefore, the interpretation of stock turn ratios should be made in conjunction with other financial metrics and industry benchmarks.
What are some common challenges in calculating accurate stock turn ratios?
+
One of the main challenges in calculating accurate stock turn ratios is obtaining reliable and up-to-date data. Accurate inventory valuation and cost of goods sold (COGS) calculations are crucial for precise ratio determination. Additionally, businesses with complex supply chains or multiple product lines may face challenges in aggregating data and calculating average inventory values. It’s important to ensure data integrity and consistency to obtain accurate stock turn ratio calculations.