Tendered For Delivery Mean
In the world of logistics and supply chain management, the term "tendered for delivery" holds significant importance. It represents a critical stage in the journey of goods from the point of origin to their final destination. Understanding what "tendered for delivery" means is essential for businesses, consumers, and anyone involved in the intricate process of shipping and receiving goods.
This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the intricacies of the term "tendered for delivery," offering a deep dive into its definition, its role in the supply chain, and its impact on various stakeholders. By exploring real-world examples, industry insights, and practical applications, we'll demystify this crucial phase of the shipping process, ensuring a clearer understanding for all.
Understanding Tendered for Delivery

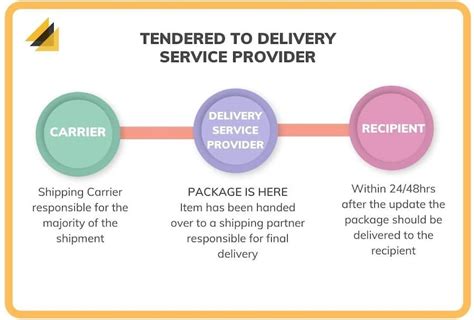
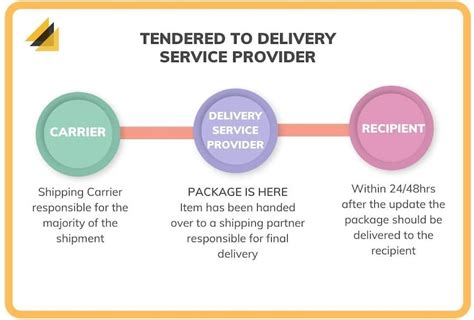
The phrase “tendered for delivery” is a specific term used in logistics and shipping to describe the point at which a shipment is officially offered to a transportation carrier for delivery. It signifies the formal initiation of the delivery process, marking a critical transition in the journey of goods from their origin to their intended recipient.
This process is a key milestone in the supply chain, indicating that the shipment has been prepared, packaged, and is now ready to be picked up by the chosen carrier. It is a moment of truth for both the shipper and the carrier, as it sets the wheels in motion for the physical transportation of goods, often across great distances.
The tendering process typically involves a set of standardized procedures and documentation. The shipper, who is responsible for initiating the tender, must ensure that all necessary paperwork is in order and that the shipment meets the carrier's requirements. This includes accurate and detailed shipping information, proper packaging, and compliance with any relevant regulations.
Once the shipment is tendered, the carrier assumes responsibility for its safe and timely delivery. This transition of responsibility is a crucial aspect of the tendering process, as it defines the scope of liability and accountability for both parties involved.
The Role of Technology in Tendering
In today’s digital age, the tendering process has been significantly streamlined and enhanced through the use of advanced technologies. Electronic data interchange (EDI) and other digital platforms have revolutionized the way shipments are tendered, making the process more efficient, accurate, and transparent.
For instance, shippers can now use online portals to enter shipment details, track the status of their tender, and receive real-time updates on the progress of their deliveries. Carriers, on the other hand, can utilize these platforms to manage their pickup schedules, optimize routes, and provide accurate ETAs (estimated time of arrival) to shippers and recipients.
Furthermore, the integration of GPS tracking and telematics has added a new dimension to the tendering process. Shippers can now monitor the location and status of their shipments in real time, gaining valuable insights into the delivery process and enabling them to make informed decisions regarding their supply chain operations.
| Key Technology Enhancements in Tendering |
|---|
| Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) |
| Online Tendering Portals |
| GPS Tracking and Telematics |
| Real-time Shipment Updates |
The Impact on Stakeholders
The tendering process has a profound impact on various stakeholders in the supply chain ecosystem. For shippers, it represents a critical juncture where their goods transition from their direct control to that of the carrier, and they must ensure that the tendered shipment meets all necessary standards.
From the carrier's perspective, tendering marks the beginning of their operational involvement. It is a moment of high importance, as it sets the tone for the entire delivery process and can significantly impact their reputation and efficiency.
For recipients, the tendering process provides transparency and clarity regarding the expected arrival of their goods. It allows them to plan their operations accordingly, whether it's managing inventory levels, scheduling personnel, or coordinating with other supply chain partners.
The Tendering Process in Action
To illustrate the tendering process in real-world scenarios, let’s explore a few practical examples:
Example 1: E-commerce Retailer
An e-commerce retailer receives an order for a set of kitchen appliances from a customer in a different state. The retailer, acting as the shipper, prepares the shipment by packaging the appliances securely and generating the necessary shipping documents. They then tender the shipment to a freight carrier, providing them with all the required details and paperwork.
Once tendered, the carrier assumes responsibility for the shipment. They pick up the appliances from the retailer's warehouse, transport them across state lines, and deliver them to the customer's doorstep. Throughout the process, the retailer can track the shipment's progress, ensuring that it reaches its destination on time and in good condition.
Example 2: International Freight Forwarder
An international freight forwarder is hired by a manufacturer to ship a large consignment of automotive parts to a distributor in a foreign country. The forwarder, acting as the shipper, coordinates with the manufacturer to receive the goods, ensure their compliance with international shipping regulations, and generate the necessary documentation.
After tendering the shipment to an ocean freight carrier, the forwarder tracks its progress as it travels across the ocean. Upon arrival at the destination port, the carrier handles the customs clearance and delivers the parts to the distributor. The forwarder's effective management of the tendering process ensures a smooth and efficient international shipment, contributing to the overall success of the supply chain.
Example 3: Local Delivery Service
A local bakery receives an order for a custom cake to be delivered to a nearby event venue. The bakery, acting as the shipper, prepares the cake in a specialized packaging to ensure its freshness and integrity during transport. They then tender the cake to a local delivery service, providing them with the venue’s address and other relevant details.
The delivery service, equipped with real-time GPS tracking, picks up the cake and delivers it to the event venue within the agreed-upon time frame. The bakery can monitor the delivery progress, receiving notifications when the cake is picked up and when it is successfully delivered. This level of visibility and control over the tendering process enhances the bakery's customer service and reputation.
Key Considerations for Effective Tendering
To ensure a successful tendering process, there are several key considerations that shippers and carriers should keep in mind:
- Accurate and Complete Documentation: Shippers should ensure that all necessary paperwork is in order, including shipping labels, bills of lading, and any special instructions or requirements. Carriers, on the other hand, should verify the accuracy of the provided documentation to avoid delays and miscommunications.
- Timely Tendering: Tendering shipments as early as possible can help carriers optimize their routes and schedules, leading to more efficient deliveries. Shippers should aim to tender their shipments well in advance of the desired delivery date to allow for any potential delays or unforeseen circumstances.
- Communication and Coordination: Effective communication between shippers and carriers is vital. Shippers should keep carriers informed about any changes or updates to the shipment, while carriers should provide regular status updates and ETAs to maintain transparency.
- Compliance with Regulations: Shippers must ensure that their shipments comply with all relevant regulations, including those related to packaging, labeling, and hazardous materials. Carriers, too, should be well-versed in these regulations to avoid legal issues and safety hazards.
- Utilizing Technology: Shippers and carriers should leverage the power of technology to streamline the tendering process. From online portals for easy shipment management to GPS tracking for real-time visibility, technology can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of tendering.
The Benefits of Efficient Tendering
Efficient tendering offers a range of benefits to all stakeholders involved in the supply chain:
- Improved Delivery Times: By tendering shipments early and managing the process effectively, carriers can optimize their routes and schedules, leading to faster and more reliable deliveries.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Timely and accurate tendering ensures that shipments reach their destinations as expected, meeting customer expectations and enhancing their overall satisfaction.
- Reduced Costs: Efficient tendering can lead to cost savings for both shippers and carriers. Shippers can benefit from reduced storage costs by tendering shipments promptly, while carriers can optimize their operations, resulting in lower fuel consumption and improved resource utilization.
- Increased Visibility: Technology-driven tendering processes provide real-time visibility into the shipment's journey, allowing all stakeholders to track its progress and make informed decisions.
- Improved Supply Chain Efficiency: A well-managed tendering process is a cornerstone of an efficient supply chain. It enables better inventory management, reduces the risk of stockouts, and enhances overall supply chain resilience.
Future Trends in Tendering
As technology continues to advance and supply chain dynamics evolve, the tendering process is likely to undergo further transformations. Here are some future trends to watch for:
AI and Machine Learning
The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms into tendering processes can bring about significant improvements. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to optimize routes, predict delivery times with greater accuracy, and identify potential disruptions before they occur. By leveraging AI, tendering can become even more efficient and predictive.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the tendering process by providing a secure and transparent platform for documenting and tracking shipments. It can enhance traceability, reduce paperwork, and streamline the tendering process, making it more secure and efficient.
Sustainable Practices
With growing concerns about environmental sustainability, the tendering process may see an increased focus on eco-friendly practices. This could involve the use of electric vehicles for local deliveries, optimizing routes to reduce carbon emissions, and adopting sustainable packaging solutions.
Last-Mile Innovations
The last mile of the delivery process, where the shipment reaches its final destination, is often the most challenging. Innovations in this area, such as drone deliveries and autonomous vehicles, could transform the tendering process, making it faster and more efficient, especially for time-sensitive shipments.
What happens if a shipment is not tendered on time?
+If a shipment is not tendered on time, it can lead to delays in the delivery process. Shippers may incur additional costs for storage or late fees, while carriers may face challenges in optimizing their routes and schedules. To avoid such issues, it is crucial for shippers to plan and tender their shipments well in advance.
How can technology enhance the tendering process for small businesses?
+Technology, such as online tendering platforms and GPS tracking, can greatly benefit small businesses by providing them with the tools to manage their shipments efficiently. These platforms offer real-time visibility, simplified documentation processes, and better control over the delivery process, helping small businesses compete in a global market.
What are the key challenges in tendering international shipments?
+Tendering international shipments comes with unique challenges, including navigating complex customs regulations, managing different currency rates, and dealing with varying transportation modes. To overcome these challenges, shippers often rely on experienced freight forwarders who can provide expert guidance and streamline the international tendering process.