What Is F O B Shipping

In the world of international trade and logistics, FOB shipping is a widely used term that plays a crucial role in defining the responsibilities and costs associated with transporting goods from one country to another. FOB, an acronym for "Free On Board" or sometimes "Freight On Board," is a set of international commercial terms that outlines the point at which the ownership and liability of goods transfer from the seller to the buyer during international shipping.
Understanding FOB Shipping

FOB shipping is a vital component of international trade, ensuring a smooth and efficient transfer of goods between countries. It is a term that has been standardized by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) and is governed by the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms), which are a set of rules and guidelines designed to reduce misunderstandings and disputes in international trade.
The FOB shipping concept is particularly relevant when discussing ocean freight, where the transfer of goods from the seller to the buyer can be complex due to the involvement of various parties, such as shipping lines, freight forwarders, and customs authorities.
Key Aspects of FOB Shipping
FOB shipping involves several key elements that define the responsibilities and risks associated with the transportation of goods:
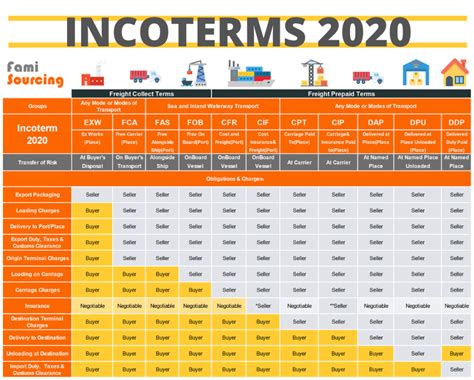
- Transfer of Ownership: The most significant aspect of FOB shipping is the transfer of ownership. The seller is responsible for the goods until they are loaded onto the vessel at the port of shipment. Once the goods are loaded, the buyer assumes ownership, and any risks associated with the goods during transit fall on the buyer.
- Cost Allocation: FOB shipping also determines the allocation of costs. The seller is responsible for all costs and expenses incurred up to the point of loading, including packaging, inland transportation to the port, and port handling fees. The buyer, on the other hand, is responsible for all costs and expenses incurred after the goods are loaded, including ocean freight, port charges at the destination, customs duties, and inland transportation to the final destination.
- Documentation: FOB shipping requires the seller to provide certain documents to the buyer. These typically include the Bill of Lading, which serves as a contract of carriage and a receipt for the goods, and other necessary trade documents such as commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
- Risk Management: By specifying the point of transfer of ownership and liability, FOB shipping helps manage risks effectively. The seller is relieved of liability once the goods are loaded, and the buyer assumes the risks associated with the goods during transit, including damage, loss, or theft.
| FOB Shipping: Key Responsibilities | Seller | Buyer |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Up to loading | After loading |
| Cost | Up to loading | After loading |
| Risk | Up to loading | After loading |

Different Types of FOB Shipping
While the basic concept of FOB shipping remains consistent, there are variations in how it is implemented based on the specific trade requirements and shipping scenarios.
FOB Origin
In an FOB Origin scenario, the seller’s responsibility ends as soon as the goods are loaded onto the vessel at the port of shipment. The buyer assumes all risks and costs associated with the goods from that point onwards. This type of FOB is often used when the buyer wants to take control of the shipping process and manage the transportation to the destination port.
FOB Destination
FOB Destination, on the other hand, shifts the responsibility for the goods to the buyer only once they have arrived at the port of destination. The seller retains ownership and liability until the goods are unloaded from the vessel at the destination port. This arrangement is favorable for buyers who want to ensure that the goods are delivered safely to the destination before taking on the costs and risks.
FOB Ex-Works
FOB Ex-Works, also known as EXW, is a variation of FOB where the seller’s responsibility is limited to making the goods available at their premises or a designated location. The buyer is responsible for arranging and paying for all transportation, including loading the goods onto the vessel at the port of shipment. This type of FOB provides the buyer with the most control over the shipping process but also carries the highest level of risk and cost.
The Impact of FOB Shipping on International Trade
FOB shipping plays a critical role in facilitating international trade by providing a clear framework for the transfer of goods, ownership, and liabilities. It helps reduce uncertainties and disputes by defining the roles and responsibilities of buyers and sellers at each stage of the shipping process.
For buyers, FOB shipping offers flexibility in managing the shipping process and controlling costs. They can choose to take on more responsibilities and risks by opting for FOB Origin or FOB Ex-Works, which may result in lower shipping costs. On the other hand, FOB Destination provides buyers with the assurance that the goods will be delivered safely to the destination before they assume ownership and costs.
Sellers, on the other hand, benefit from FOB shipping by clearly delineating their responsibilities and risks. They can focus on their core competencies, such as production and packaging, and rely on the buyer to manage the shipping process effectively. This allows sellers to optimize their operations and reduce their exposure to risks associated with international shipping.
Overall, FOB shipping is a fundamental concept in international trade that ensures a fair and efficient transfer of goods between countries. By understanding the nuances of FOB shipping and its variations, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their supply chain processes and manage risks effectively.
What is the difference between FOB shipping and CIF shipping?
+FOB and CIF are two different international commercial terms that define the responsibilities and costs associated with shipping goods. FOB, as discussed earlier, transfers ownership and liability to the buyer once the goods are loaded onto the vessel at the port of shipment. CIF, on the other hand, extends the seller’s responsibility to include insurance and freight costs. In CIF shipping, the seller arranges and pays for insurance and freight up to the destination port, and the buyer assumes ownership and risks from that point onwards.
Who is responsible for arranging the shipping in FOB shipping?
+In FOB shipping, the responsibility for arranging the shipping typically falls on the buyer. While the seller may assist in providing shipping documentation and coordinating with the shipping line, the buyer is responsible for selecting the shipping method, arranging transportation to the port of shipment, and managing the shipping process from the point of loading onwards.
Can FOB shipping be used for air freight as well as ocean freight?
+Yes, FOB shipping can be applied to both air freight and ocean freight. The principles of FOB shipping remain the same regardless of the mode of transportation. However, the specific terms and responsibilities may vary slightly due to the differences in the logistics involved in air freight and ocean freight.